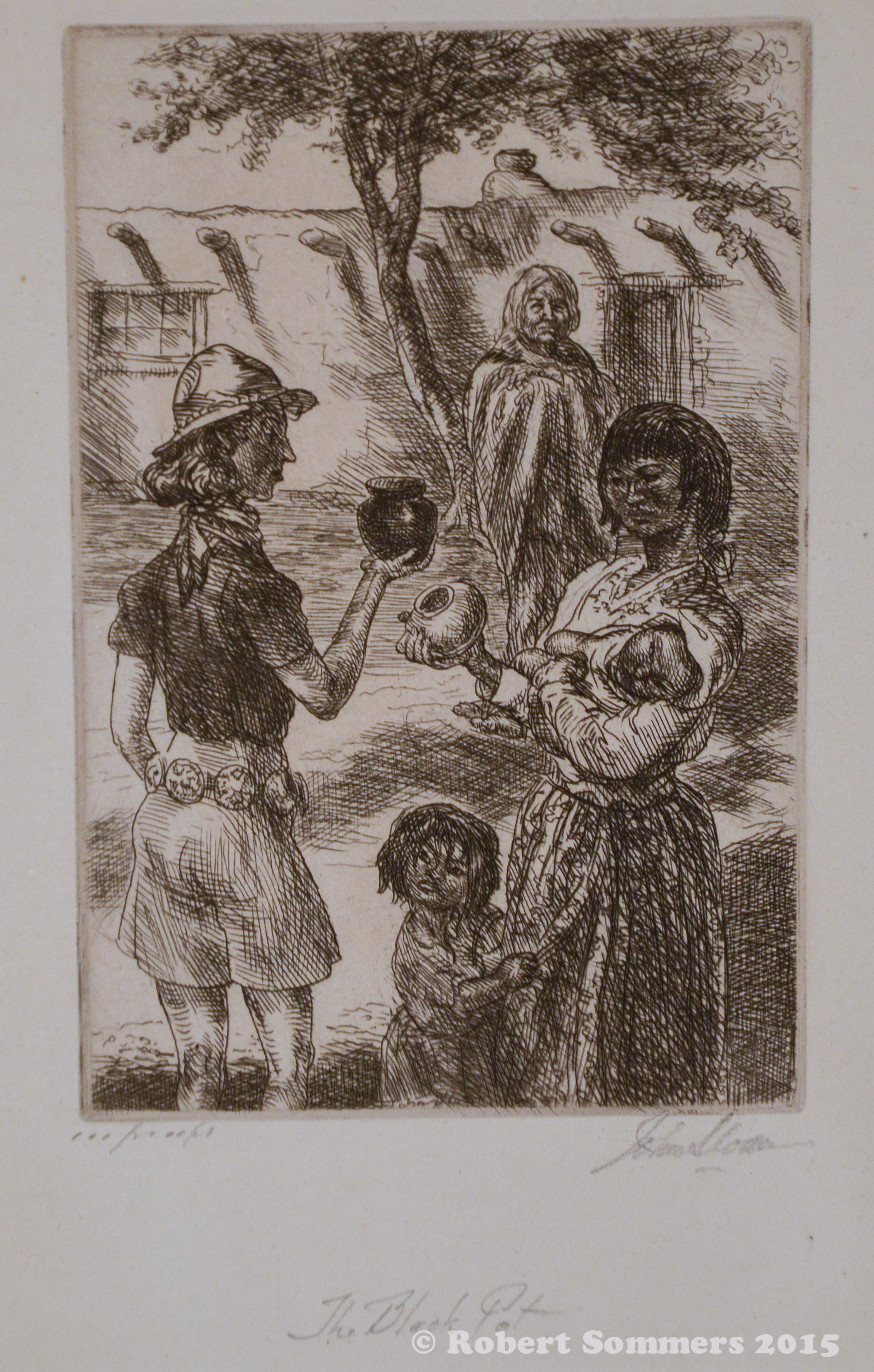John Sloan (1871-1951) The Black Pot (M. 299), 1937
Etching printed on laid paper, signed in pencil and annotated ‘100 proofs’, from the edition of 100, second (final) state, with full margins, rich, excellent impression in very good condition aside from slight toning. Framed.
6 x 4″ – sheet 11 x 8″ $2500 A wry look at the early New Mexico tourist trade.
Born in Lock Haven, Pennsylvania, John Sloan became one of the major early 20th- century figures in New York, pioneering the Social Realist movement with Robert Henri and his circle. He was also an illustrator and early eastern painter in the Southwest.
Sloan moved with his family to Philadelphia where he attended Central High School and became a close friend of William Glackens. He worked for a print dealer and as illustrator for the Philadelphia Inquirer and the Philadelphia Press. He also studied at the Pennsylvania Academy with Thomas Anshutz and met Robert Henri.
In 1904, he moved to New York and while continuing as an illustrator, became a part of Henri’s circle of urban realists. He was an avid walker who continually strolled the streets for subject matter, especially exploring Greenwich Village and the Lower East Side. His work with great humanitarian bent flourished especially during this time because he was so committed emotionally to his subject matter.
He joined the Socialist Party in 1910 and espoused utopian ideas of equality but was never a political activist. However, from 1912 to 1916, he was art editor of the party’s monthly periodical The Masses, and his skillful illustrations elevated the quality of the publication. The realities of World War I caused him, like so many, to become disenchanted with hard-line socialism.
He taught at the Art Students League, and his students included Reginald Marsh, Raphael Soyer, and Alexander Calder.
Opposing the traditional hold that the National Academy had over the art world in America, he exhibited as one of “The Eight” in 1908 at the Macbeth Gallery. In 1913, he was much affected by the Armory Show exhibition of modernist painting, particularly the Post-Impressionist, Fauve, and Cubist works and after that year became experimenting with more radical painting styles. He was also an avid etcher.
Influenced by his friend Henri, who had spent summers of 1916 and 1917 in New Mexico, Sloan and his wife Dolly first visited Santa Fe in 1919. From that time, he made several painting trips to the Southwest and was active in the Santa Fe colony and in getting other eastern artists to head West. Unlike many of his contemporaries there, he refused to paint romanticized views of the Mexican and Indian culture. He served as President of the Exposition of Indian Tribal Arts in the 1930s and lobbied the Society of Independent Artists to include work by Native Americans in their exhibitions.
In 1944, Sloan married Helen Farr, who had been one of his students, and after her husband’s death in 1951, she devoted herself to turning his estate into a philanthropic instrument. The largest benefactor was the Delaware Art Museum, which recieved more than 5000 works including painting representing every phase of his career and his archival papers. With these acquisitions, the Museum became the leading repository for the study of Sloan. In honor of the ongoing support by Helen Farr Sloan, museum representatives named its library the Helen Farr Sloan Library.